A Comprehensive Guide to Diamond Color Scale: Diving into Brilliance
November 17th, 2023 / Alese Oldenburg
A diamond’s color grade is largely considered to be one of the most important characteristics when assessing a diamond to purchase, usually a priority only secondary to diamond shape. Even subtle differences in diamond color grading can dramatically impact its value. For example, when comparing diamond clarity, weight, and if two diamonds have the same clarity, weight, and cut, the slightest hint of color in one will decrease its value.
Many of the diamonds sold today are nearly colorless, but in reality, the normal range of color for diamonds can vary from absolutely colorless to light yellow or brown. This is why the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) developed a diamond color scale, which is now widely accepted as the industry standard color grading system. Whether looking for a diamond engagement ring or other diamond alternative jewelry, understanding the GIA color scale is key to properly informing any of your diamond purchases. Follow along as we break down the diamond grading color system and determine the best diamond color.
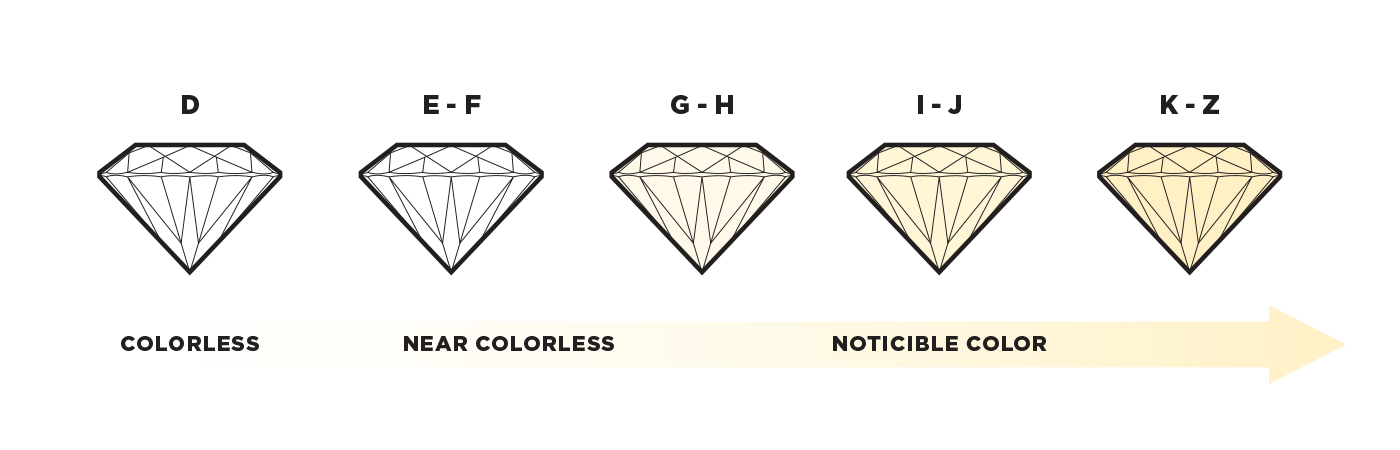
The Diamond Color Chart
The color of a diamond is an evaluation of the absence of color. A chemically pure, structurally perfect diamond has absolutely no hue, which results in it having a much higher value since that level of diamond quality is so rare. The GIA’s diamond grading color system requires the presence or absence of color in a single stone to be measured in comparison to master stones of previously established colors.
The GIA diamond grading scale starts with the letter D, which represents a perfectly colorless diamond and continues to the letter Z, with each letter in between delineating an increasing presence of color intensity. The average person can detect the difference between a grade D color diamond and that of a Z color diamond because of the significant difference between the opposite ends of the scale. However, generally, measurements must take place under explicitly controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions by a trained professional, as subtle differences may be undetectable to an untrained eye. The diamond color scale can be further broken down into five categories with color grades that range from colorless to light color.
Colorless Diamonds
Wondering what is a colorless diamond? Grades D, E, and F on the scale make up the Colorless diamonds. Only an experienced gemologist will be able to detect the precise differences between these three gradings, but the corresponding values will differ greatly. Grade D diamonds are extremely rare and colorless, while E color diamond and F color diamond grades contain minute traces of color largely unnoticeable to the everyday consumer.
Near Colorless Diamonds
G, H, I, and J are the grades considered Near Colorless. These diamonds have a slightly warm and yellow color and tone that is difficult for consumers to detect unless compared side-by-side with a diamond of a higher grade. Generally speaking, the faint yellow hues pair well with gold-tone settings.
Faint Color Diamonds
Grades K, L, and M make up the Faint category of colors. At this point, you may begin to be able to detect the tint of the diamond without prior training, since they possess a visible yellow tint. Due to the color variation, diamonds of this grade are much less desired, resulting in steep diamond price drops from the previous category of the color chart.
A grade K color diamond can cost as much as 50% less than a grade G color diamond. For this reason, many diamond stores and dealers don’t hold diamonds below the I-J color in stock, However, some people find the warm coloration appealing and may be interested in diamonds of these grades when designing a vintage-style ring.
Very Light Color
N, O, P, Q, and R are the grades that make up the Very Light category and have a strongly notable color. The color can vary from yellow to brown tint and is sometimes referred to as “top light brown” within the industry. These diamonds have very low demand, which results in extremely low prices (possibly the lowest in the industry).
Light Color
All other grades from S to Z are considered Light. Interestingly, Light-colored diamonds – specifically those beyond a U grade – usually have greater demand than Very Light diamonds. This is because the slightly stronger color is seen simply as a yellow stone, rather than an off-color diamond. However, diamonds of this grade are still not considered to be fancy color diamonds.

Exploring Diamond Color Dynamics
Diamond prices are largely dependent on the diamond color grade. However, several components can have an impact on the visible appearance of a diamond’s body color and play a role in what makes a diamond sparkle. These should be considered especially when assessing diamonds that are only a few grades apart on the GIA color scale.
Role of Ring Settings: Selecting a ring setting that pairs well with your diamond and is similar in tone can help neutralize any hues in the diamond itself. For example, choosing a yellow gold setting for a Near Colorless diamond will effectively absorb the yellow tint contained within the diamond. Likewise, a colorless diamond may look the brightest set in white gold or platinum to highlight its pure lack of color.
Influence of Diamond Shapes: Certain shapes of diamonds can show or hide color to varying degrees. A diamond cut like a round or princess, for example, reflects more light, which in turn masks more color. Step-cut diamonds such as emerald or Asscher, however, may highlight any hues of color because these cuts have fewer facets. This results in larger windows into the diamond to see Color. Similarly, fancy-shaped cuts, like pear and marquise, can also have slightly more concentrated color at their pointed ends.
Diamond Size and Color: Simply put, color is easier to see in a larger diamond shape. If you are considering purchasing a lower-grade stone, be careful to also make carat size comparisons. If you’re looking above 1 carat, you should look for a grade H color diamond or better.
Fluorescence: UV Radiance of Diamonds: When exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, many diamonds emit a visible light known as fluorescence. And despite being undetectable by the human eye, UV radiation is all around us, contained in sunlight and emitted by fluorescent lighting. The fluorescence of a diamond can be seen under the right conditions and is most often blue. In rare cases, it can be white, yellow, or orange. If a diamond’s blue fluorescence is strong enough, it can make a light yellow diamond appear close to colorless when exposed to UV rays like sunlight. However, if a diamond’s fluorescence is too strong, it can make the diamond look cloudy, which can then lower its value.
The Best Color Diamonds
Unfortunately, there is no straight answer to this question, as it will mostly depend on what is important to you as the buyer. Colorless diamonds, grades D-F, will always represent the highest quality stones that you can get. However, they are rare and therefore quite expensive. Near Colorless diamonds, grades G-H, represent the best value if you are on a budget. Due to their slightly lower grade and the presence of some nearly undetectable color intensity, these diamonds are generally more affordable, with hues only a trained professional will be able to see. If you are looking for something small and would like a yellow gold setting, an even lower color grade diamond or colored gemstone may be more suitable for your needs and budget.
If you’re looking for a more affordable diamond ring and don’t want to compromise on quality or beauty, a lab diamond alternative can be a wonderful option to consider. Many wonder, are lab diamonds real? Lab diamond alternatives such as Nexus Diamonds™ are created in a lab so that every diamond alternative has the qualities imitative of a perfect natural diamond. By selecting one of these diamond alternatives for your engagement ring, diamond earrings, or diamond jewelry, you can get a D-grade simulant stone at a fraction of the cost, due to the methods of producing lab made diamonds.

Fancy Colored Diamonds
One in every 10,000 diamonds possesses natural color and is considered a “fancy-colored diamond”. Each fancy color diamond is graded on a separate scale from white diamond or colorless diamond. The more intense and evenly distributed the color is, the more rare and valuable the diamond is. In some cases, a colored diamond can be even more valuable than a white diamond. The specific color of a fancy colored diamond is the most important characteristic used to evaluate the value, closely followed by diamond clarity, carat, and then diamond cut.
The unique colored diamonds grading scale was also developed by the GIA and measures the following increases in color strength:
- Faint,
- Very Light,
- Light,
- Fancy Light,
- Fancy,
- Fancy Intense,
- Fancy Vivid,
- Fancy Dark
- Fancy Deep
Fancy Vivid and Fancy Deep are typically considered the most valuable. The existing base colors for fancy-colored diamonds include red diamond, blue, pink, green, purple, violet, gray diamond, brown diamond, orange diamond, black and yellow diamond.
The Diamond Nexus Promise
Diamond Nexus developed a patented diamond alternative to simulate the look, wear, and feel of natural diamonds with superior quality. Every Nexus Diamond alternative has a D color grade with Internally Flawless (IF) diamond clarity and an Ideal Cut for maximum brilliance and fire. In this way, you can ensure that your diamond alternative will be perfectly colorless, but at a fraction of the cost. Our stones are also created so that they’ll never chip, crack, or become discolored or cloudy with normal wear. Our Lifetime Stone Guarantee ensures that if anything does happen to your stone, we will replace it for free, forever.

At Diamond Nexus, we believe that you shouldn’t have to compromise on quality if you’re on a budget or have to choose between having the ring of your dreams or an unforgettable honeymoon. Find a perfect diamond that fits your budget and sparkles with the brilliance you’ve always pictured.
*Diamond Nexus strives to provide valuable information while being clear and honest about our products. The Nexus Diamond™ alternative is a patented lab-created diamond simulant that, among all simulants, most closely imitates the look, weight, and wear of a mined diamond, with two exceptions – it is perfect in every way, and it costs significantly less. Price points and environmental facts expressed in this blog were taken from popular online retailers and may vary. Learn more about the environmental impact of mining by visiting our blog: blog.

